
Your skin is the body's largest organ, and it performs one very significant function: keeping the outside world out. And while doing this, it is also one of the first organs to reflect unhealthy signs. Whether it's a benign rash or something more fatal, knowledge of common skin conditions is the gateway to your skin's overall well-being. This article will walk you through the most prevalent skin diseases, their treatment, skin health, and how patient awareness, prevention tips, and safety protocols can assist. We'll also cover the lifestyle facts of these diseases so that you know and are empowered.
They affect millions of people across the United States. They can be as fleeting as a nuisance or as chronic as a disease. Some are temporary and cure themselves without medication, while others require ongoing treatment by a dermatologist. Understanding the cause, the symptom, and the treatments is half the battle when it comes to healthier skin.
Patient teaching is needed here. Most individuals wait for a bump or rash to go away on its own. However, complications can be prevented with early intervention. Without injury, treatment with proper diagnosis can be done and can prevent the further development of symptoms or infection. Teaching about these common dermatoses will also allow you to view principles of prevention that prevent them before they occur.
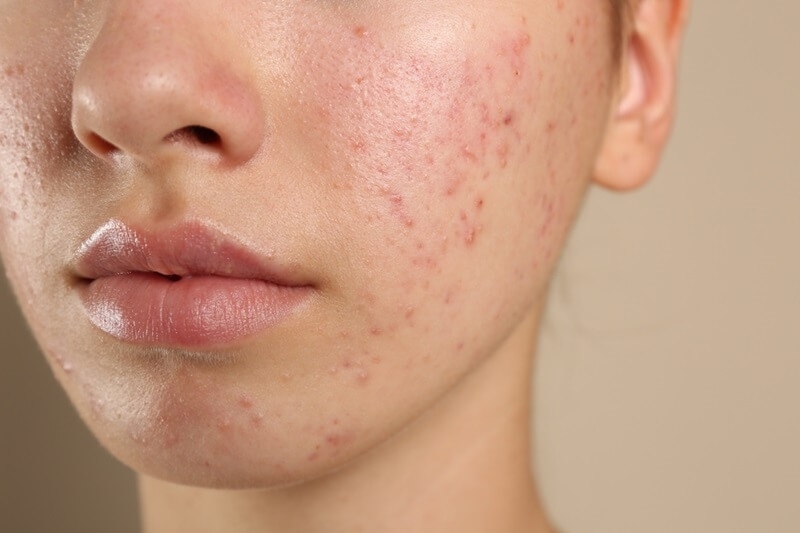
Acne is also among the most common skin conditions, but primarily in youth and young adults, although it may occur in any person of any age. Acne occurs because of the blockage of hair follicles by oil and dead skin cells in the skin, leading to pimples, blackheads, or cysts.
Skin is involved if the acne is either chronic or severe, with scarring or hyperpigmentation. It is not harmful but does interfere with lifestyle, which can impact self-esteem and social function. Patient education on treatment is of the highest priority to avoid psychological disturbance.
Prevention includes face washing, not scrubbing excessively, and applying non-comedogenic cosmetics. Treatment can vary from topical creams to oral medication or in-clinic treatments such as chemical peels. Adhering to medical advice results in safe treatment and can go a long way towards improving skin health in the long term.
Atopic dermatitis or eczema is another of the most common skin diseases, especially in children, but also in adults. It leads to dry, scaly, inflamed skin and can flare up unpredictably.
Eczema also causes a significant lifestyle burden as flare-ups occur at irregular frequencies and are usually inconvenient. Children lose sleep, and adult workers miss work or experience social embarrassment. Precipitant identification by the patient—such as allergens, stress, or irritating clothing—is important.
For improved skin, dermatologists normally suggest frequent moisturizing, avoiding the known triggers, and topical immunomodulators or corticosteroids as needed. Precautions include keeping the skin moist and using gentle, fragrance-free products. Treating it early allows safe management and bars the chronic condition from forming.
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition that speeds up the life cycle of the skin cells, creating scaly red plaques. It is one of the more chronic of the common dermatologic conditions and typically must be managed in the long term.
Psoriasis has a significant psychological effect as well, affecting one's own body image, relationships, and even job prospects in cases of eruptions being visible or symptomatic. It is necessary to educate the patient about its nature—that it is an autoimmunity disorder and not infection—so that there can be no stigma attached.
Skin condition is kept under control by following treatment as ordered by dermatologists like topical treatment, phototherapy, or biologic treatment. Preventive strategies like stress management, not smoking, and limited use of alcohol might minimize the number of flare-ups. Planned care and follow-up are the characteristics of safe care.
Rosacea is a skin condition of the face that is marked by redness and visible blood vessels in the face. It has a tendency to cause small pimples, which have pus. It is one of the prevalent skin diseases of individuals with fair skin primarily in adults.
Although rosacea is not a life-threatening disease, it still has a tremendous lifestyle impact due to the visibility of redness on the face. Informing the patient that rosacea can be managed can get individuals into treatment rather than covering it up.
Prevention is by avoidance of precipitating factors like hot drinks, spicy food, sun, alcohol, or close intimacy. Treatment is by topical creams, oral antibiotics, or laser. Flare control with precautions provides safety during treatment and improves long-term skin integrity.
Yeast infection, Ringworm, and Athlete's foot are fungal infections of the skin, nail, or scalp. They are very common skin conditions and are generally contagious from infected surfaces or personal contact.
They can compromise the skin's integrity by causing itching, redness, or fissuring. The lifestyle impact is minimal, but if left untreated, they result in extension or recurrence. Patient hygiene education and early treatment are important.
Prevention includes dry skin, sweating clothes removal, and not sharing towels. Oral, powder, or cream antifungals are the typical medications. Taking them under medical supervision provides safe medication coupled with general skin integrity.
Contact dermatitis is a skin response to an irritant or allergen. It is one of the usual skin diseases that will clear up as soon as the offending agent is removed, but that will lead to intense itching and redness.
Lifestyle impact can be missed work days or daily discomfort if the rash is widespread. Patient education to prevent contact with allergens in personal products or workplace exposure is one way of preventing recurrence and skin integrity.
Prevention is through protective gloves, hypoallergenic preparations, and patch-testing new skin products. Mild cases are treated with over-the-counter hydrocortisone cream, but it must be prescribed in severe cases. Avoidance of triggers and early treatment give safe control.
Hives (urticaria) are itchy, raised welts that develop suddenly due to an allergy, stress, or unknown cause. They are one of the short-term skin diseases, but they can be alarming when they erupt suddenly.
They can conditionally influence the health of the skin by causing pain and inflammation. Their sudden development also influences lifestyle in the short term, particularly where public or social events are concerned. Patient awareness on precipitants such as medications or foods helps in the management of the condition.
Prevention is through avoidance of known allergens and stress reduction. Antihistamines are the treatment of choice, and a healthcare provider visit guarantees good care in the event of chronic or acute hives. Monitoring of symptoms prevents complications and guarantees healthy skin.
Shingles (herpes zoster) is a painful rash caused by reactivation of the chickenpox virus. It occurs most commonly in older adults and is one of the more severe common skin diseases, in that it can result in chronic nerve pain.
The effect of shingles on a life is devastating due to severe pain and loss activity or work. Knowing that a shingles vaccine exists can stop it from happening in the first place and result in healthier skin for the elderly.
Prevention is by immunization, stress reduction, and a healthy immune system. Antiviral medication can abbreviate the duration of the disease and restrict complications if taken early. A strict following of a physician's treatment plan ensures safe control and eliminates any possibility of residual nerve pain.
The most dangerous of all common skin diseases is skin cancer, which has a list of varieties like Basal cell carcinoma, Squamous cell carcinoma, and Melanoma. It is extremely necessary to detect it in the early stages because if left untreated, it can lead to death.
It significantly affects lifestyle, from treatment side effects to surveillance in the long term. Education of patients about skin inspection and dangers of tanning beds is needed to preserve life and maintain healthy skin.
Prevention is achieved through daily sun protection with sunscreen, shade seeking, and avoidance of sun times. Skin cancers are nearly all curable with simple surgery if they are caught early. Dermatology visits and protective behaviors must be adhered to for safe care and for healthy skin maintenance.
Patient education is a recurring issue when it comes to managing common skin conditions. They avoid treatment, deny the development, or attempt untried home remedies that will ruin their skin integrity. Being educated on symptoms, risk factors, and available treatments is empowering you to be responsible with your skin.
The health practitioners will prioritize proper diagnosis and safe treatment because wrongly treated ailments will lead to complications, infection, or scarring. There is also reduced stigma for obvious skin ailments, which can have a significant life impact on self-esteem. Having more knowledge about your skin enables you to get beneficial prevention advice as well as healthier skin in the future.
Skin diseases not only impact one's appearance, but also their emotional and mental health. The social implications of visible or painful skin diseases could be social anxiety, lost work time, or low self-esteem. Treating them with compassion and professional medical attention is the key to complete healing.
Simple habits like a good diet, proper sleep, stress management, and cleanliness can improve the health of the skin. They are also prevention tips to restrict the frequency of occurrence or severity of common skin diseases. Friends, support groups, or counselors can also cut down the emotional stress, i.e., it will be easier to carry out safe care practices.
Prevention of skin issues is always simpler than treatment. The simplest prevention guidelines are as follows:
Just as important is the observance of safe care practices, should you do get sick with a skin disease. This includes going to a competent dermatologist, and not medicating yourself, and following the regimen. The combination of prevention and patient education reduces complications and guarantees long-term skin health.
Acne, eczema, and other skin ailments are a reality, but they do not have to take over your life. Patient awareness, preventive measures, and well-documented treatment in their due proportion can help you keep your skin health in check and rein in their interference with life. Rash or chronic condition, early diagnosis and adequate treatment go a long way.
Keep in mind, your skin is a mirror of your overall well-being. Treat it kindly, do your research, and don't hesitate to bring in a professional if it's not looking exactly right. Beautiful skin is deeper than skin-deep—it's a gateway to healthy, confident living. Information on the internet changes daily, so before believing the information mentioned in this article, please confirm it through various dependable sources or consult a licensed medical practitioner.
This content was created by AI